Menu Driven Program in Java Example
Hey everyone, welcome to my new Menu Driven Program In Java Tutorial. Here you will learn to create a menu driven program using Java programming language.
But before implementing menu driven code, we need to understand about what is menu driven program, why we use it and what are the various ways to create a menu driven program in Java. So without wasting time let's gets started.
Also Read – Object Oriented Programming in Java Questions and Answers
Contents
- 1 An Introduction To Menu Driven Program In Java
- 1.1 What is a menu driven program in Java?
- 1.2 Which statement is specially used for menu driven program in Java?
- 1.3 How do you write an algorithm for a menu-driven program?
- 1.4 How do I create a menu driven program?
- 2 How To Write Menu Driven Program In Java
- 2.1 Menu Driven Program in Java for Calculator
- 2.2 Menu Driven Program in Java for String Operations
- 2.3 Menu Driven Program in Java using While Loop
- 2.4 What We Did?
- 2.5 Menu Driven Program In Java Using do-while Loop
- 2.6 Menu driven program in Java using Methods
- 2.7 How do I exit from a Menu Driven Program?
In many applications you must have seen menus. Menus are generally a collection of choice in which user can select any choice according to their interest and can perform that particular task.
So let's know a brief idea about menu driven in Java.
A menu driven program displays a list of options to take input from user. User can select and enter options displayed on screen as per his/her choice and can do whatever they want to do.
Menu driven program are very user friendly that's why most applications use this instead of command line input. The two advantage of using menu driven program is –
- The system is less prone to user error because input is via single key strokes
- Because only a limited range of characters are allowed, the way in which the input is to be entered is unambiguous.
Switch statement is used to create menu driven program because switch statement contains cases. Each case contains different functionality.
Switch statement takes user choice as input and calls the correct case related to choice so that correct task can be performed.
I hope now you have understand all about menu driven program. But still you will be thinking how to implement it. So first let's understand algorithm for a menu driven program.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | Step 1 : Start the program Step 2 : Read choice Step 3 : Repeat till a valid choice Step 3a : if choice is 1 perform task Step 3b : If choice is 2 perform task Step 3c : If choice is 3 perform task default : perform task Step 4 : Stop the program . |
We can write menu driven program in two ways –
- Write the whole program in switch-case branches.
- Create separate methods and call those methods from the switch-case branch.
So guys until now you have learned about menu driven program now its time to writing java program for it.
Menu driven program using java language is generally written with the help of switch statement. So let's implement it practically.
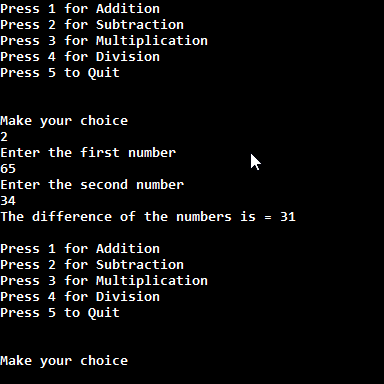
In this example, we will create a simple menu-driven program for calculation purposes of 4 essential math operations Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and division.
Code is following.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 | //Importing Saanner class import java . util . Scanner ; //Creating Class public class CalculatorMenuDrivenExample { //Creating main method public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { //Declaring all variables int a , b , c ; int choice ; Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ) ; //Creating infinite while loop while ( true ) { //Creating menu System . out . println ( "Press 1 for Addition" ) ; System . out . println ( "Press 2 for Subtraction" ) ; System . out . println ( "Press 3 for Multiplication" ) ; System . out . println ( "Press 4 for Division" ) ; System . out . println ( "Press 5 to Quit\n \n " ) ; //Asking user to make choice System . out . println ( "Make your choice" ) ; choice = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; //Creating switch case branch switch ( choice ) { //First case for finding the addition case 1 : System . out . println ( "Enter the first number " ) ; a = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter the second number" ) ; b = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; c = a + b ; System . out . println ( "The sum of the numbers is = " + c + "\n" ) ; break ; //Second case for finding the difference case 2 : System . out . println ( "Enter the first number " ) ; a = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter the second number" ) ; b = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; c = a - b ; System . out . println ( "The difference of the numbers is = " + c + "\n" ) ; break ; //Third case for finding the product case 3 : System . out . println ( "Enter the first number" ) ; a = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter the second number" ) ; b = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; c = a * b ; System . out . println ( "The product of the numbers is = " + c + "\n" ) ; break ; //Fourth case for finding the quotient case 4 : System . out . println ( "Enter the first number" ) ; a = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter the second number" ) ; b = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; c = a / b ; System . out . println ( "The quotient is = " + c + "\n" ) ; break ; //Fifth case to quit the program case 5 : System . exit ( 0 ) ; //default case to display the message invalid choice made by the user default : System . out . println ( "Invalid choice!!! Please make a valid choice. \\n\\n" ) ; } } } } |
What We Did?
- First of all, we have imported the Scanner class.
- Then created a class and given a name CalculatorMenuDrivenExample.
- Then started the main method.
- Inside main method, declared all the variable names which we used later.
- After that, I have created an infinite while loop by using true as its condition, and it will run for infinite times, and later on, we will also have the condition to exit from this infinite loop.
- Then displayed a menu.
- After that asked the user to enter their choice.
- Then created switch case branch. The first case is for finding the addition of two numbers, the second case is for finding the difference of two numbers, the third case is for finding the product of two numbers, the fourth case is for finding the quotient and the fifth case is for quitting the program.
- If the user enters the wrong choice which is not available in the menu, then a message of invalid choice will display.
Output
Now check it's output which is following.
We are taking an example where we have to write a simple menu driven program using Java for string operations. If you want to learn string operations in java then check here.
We can perform various operations on string in Java but here I am taking just 4 string operations which are following to illustrate this example.
- Length of string
- Concatenate two strings
- Comparing two strings
- String trimming
So now let's write menu driven program for string operations in Java. Code is following.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 | import java . util . Scanner ; public class StringMenuDrivenExample { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { int ch ; String str , str1 , str2 ; boolean str3 ; int length ; Scanner sc = new Scanner ( System . in ) ; // displaying the menu System . out . println ( "1: Length Of String" ) ; System . out . println ( "2: String Concatenation" ) ; System . out . println ( "3: String Comparison" ) ; System . out . println ( "4: String Trimming" ) ; System . out . println ( "5: Quit" ) ; System . out . print ( "Make your choice: " ) ; ch = sc . nextInt ( ) ; // reading user's choice switch ( ch ) { case 1 : // for length of string sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; length = str . length ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Length of string: " + length ) ; break ; case 2 : //for string concatenation sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str2 = str . concat ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nConcatenated string: " + str2 ) ; break ; case 3 : // for string comparison sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str3 = str . equals ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nComparison Of String: " + str3 ) ; break ; case 4 : // for string trimming sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str1 = str . trim ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nTrimmed String:" + str1 ) ; break ; case 5 : System . exit ( 0 ) ; default : System . out . println ( "Invalid choice!!! Please make a valid choice. \n\n" ) ; } } } |
What We Did?
- First of all we have imported Scanner class.
- Then created a class and given a name StringMenuDrivenExample.
- Then started the main method.
- Inside main method, declared all the variable names which we used later.
- Then displayed a menu.
- After that asked the user to enter their choice.
- Then created switch case branch. First case is for finding length of string, second case is for concatenation of string, third case is for comparison of strings, forth case is for trimming of string and 5 case is for exit the program.
- If the user enters the wrong choice which is not available in the menu, then a message of invalid choice will display.
Output
Now check it's output which is following.
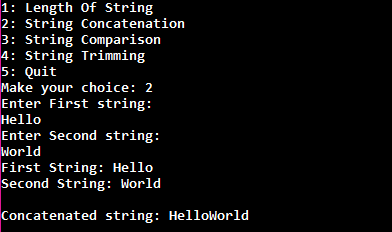
In the output, you can see user has entered choice 2 which is string concatenation. That's why second case is executed.
Now we will see how to make menu driven program using while loop in Java language.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 | import java . util . Scanner ; public class StringMenuDrivenExample { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { int ch ; String str , str1 , str2 ; boolean str3 ; int length ; Scanner sc = new Scanner ( System . in ) ; while ( true ) { // displaying the menu System . out . println ( "\n1: Length Of String" ) ; System . out . println ( "2: String Concatenation" ) ; System . out . println ( "3: String Comparison" ) ; System . out . println ( "4: String Trimming" ) ; System . out . println ( "5: Quit" ) ; System . out . print ( "\n Make your choice: " ) ; ch = sc . nextInt ( ) ; // reading user's choice switch ( ch ) { case 1 : // for length of string sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; length = str . length ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Length of string: " + length ) ; break ; case 2 : //for string concatenation sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str2 = str . concat ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nConcatenated string: " + str2 ) ; break ; case 3 : // for string comparison sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str3 = str . equals ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nComparison Of String: " + str3 ) ; break ; case 4 : // for string trimming sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str1 = str . trim ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nTrimmed String:" + str1 ) ; break ; case 5 : System . exit ( 0 ) ; default : System . out . println ( "Invalid choice!!! Please make a valid choice. \n\n" ) ; } } } } |
What We Did?
- We have used while loop whose condition statement always evaluates to true.
- Inside the while loop, we have displayed the menu and reading user's choice.
- When user will enter his/her choice then string operations will be performed according to their entered choice.
Output
Now it's time to check the output. So its outputs are as follows.
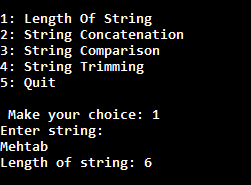
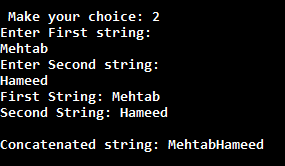
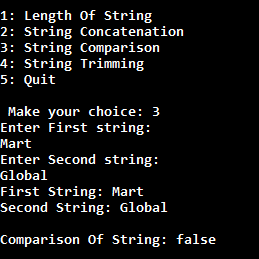
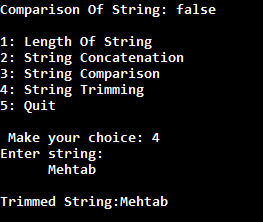
In a menu driven program, generally we have to execute body of menu loop at least once. In this case do-while loop is very helpful to create menu driven program.
So the code of menu driven system using do-while loop in Java is following. Let's write and execute this code to check the output.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 | import java . util . Scanner ; public class StringMenuDrivenExample { public static void main ( String args [ ] ) { int ch ; String str , str1 , str2 ; boolean str3 ; int length ; Scanner sc = new Scanner ( System . in ) ; do { // displaying the menu System . out . println ( "\n1: Length Of String" ) ; System . out . println ( "2: String Concatenation" ) ; System . out . println ( "3: String Comparison" ) ; System . out . println ( "4: String Trimming" ) ; System . out . println ( "5: Quit" ) ; System . out . print ( "\n Make your choice: " ) ; ch = sc . nextInt ( ) ; // reading user's choice System . out . println ( "\n" ) ; switch ( ch ) { case 1 : // for length of string sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; length = str . length ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Length of string: " + length ) ; break ; case 2 : //for string concatenation sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str2 = str . concat ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nConcatenated string: " + str2 ) ; break ; case 3 : // for string comparison sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter First string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter Second string: " ) ; str1 = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str3 = str . equals ( str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "First String: " + str ) ; System . out . println ( "Second String: " + str1 ) ; System . out . println ( "\nComparison Of String: " + str3 ) ; break ; case 4 : // for string trimming sc . nextLine ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter string: " ) ; str = sc . nextLine ( ) ; str1 = str . trim ( ) ; System . out . println ( "\nTrimmed String:" + str1 ) ; break ; case 5 : System . exit ( 0 ) ; default : System . out . println ( "Invalid choice!!! Please make a valid choice. \n\n" ) ; } } while ( ch < '1' || ch > '5' ) ; } } |
Output
So the output of the above code is following.
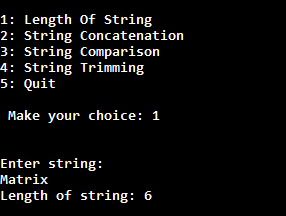
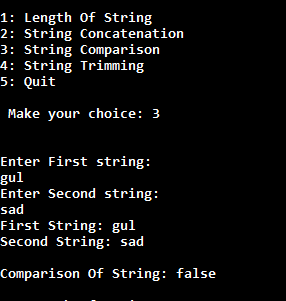
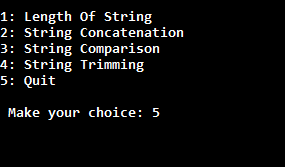
In this case, what we will do that when the user makes any choices, then we will call a specific method inside the switch case for that particular choice.
For the example purpose, I am going to find the area of rectangle, square and circle. If the user makes a choice first, then the area of the rectangle will be evaluated. If the user makes choice second, then the area of the square will be evaluated. If the user makes a choice third, then the area of the circle will be evaluated.
So the code of menu driven system using method in Java is following. Let's write and execute this code to check the output.
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 | //Importing Scanner class import java . util . Scanner ; //Creating Class public class MenuDrivenUsingFuction { //Declaring all the Variables and Scanner class static Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( System . in ) ; static double length , breadth , side , radius , area ; static double pi = 3.14 ; static int choice ; //Creating main method public static void main ( String [ ] args ) { //Asking user to make a choice System . out . println ( "Enter 1 for Area of Rectangle" ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter 2 for Area of Square" ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter 3 for Area of Circle" ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter 4 to Quit" ) ; choice = scanner . nextInt ( ) ; //Creating switch block switch ( choice ) { //Creating cases and calling methods as per the users choice case 1 : rectangleArea ( ) ; break ; case 2 : squareArea ( ) ; break ; case 3 : circleArea ( ) ; break ; case 4 : System . exit ( 0 ) ; default : System . out . println ( "You have entered the wrong choice\n" ) ; } } //Method to evaluate the Area of Rectangle public static void rectangleArea ( ) { System . out . println ( "Enter the length of the Rectangle" ) ; length = scanner . nextDouble ( ) ; System . out . println ( "Enter the breadth of the Rectangle" ) ; breadth = scanner . nextDouble ( ) ; area = length* breadth ; System . out . println ( "The Area of the Rectangle = " + area + "square unit" ) ; } //Method to evaluate the Area of Square public static void squareArea ( ) { System . out . println ( "Enter the side of the Square" ) ; side = scanner . nextDouble ( ) ; area = side* side ; System . out . println ( "The area of the Square = " + area + "square unit" ) ; } //Method to evaluate the Area of Circle public static void circleArea ( ) { System . out . println ( "Enter the readius of the Circle" ) ; radius = scanner . nextDouble ( ) ; area = pi* radius* radius ; System . out . println ( "The area of the Circle = " + area + "square unit" ) ; } } |
What We Did?
- First of all we have imported Scanner class.
- Then created a class and given a name MenuDrivenUsingFuction.
- Inside the class, we declared all the variables and created a Scanner class which we used later.
- Then started the main method.
- Inside the main method, displayed a menu and asked the user to make his choice.
- Then created switch case branch. If The user makes choice 1, then we will call the method to evaluate the area of the Rectangle, if the user makes choice 2, then we will call the method to evaluate the area of the Square, if the user makes choice 3, then we will call the method to evaluate the area of the Circle, if the user makes choice 4 then the program will quit, and if the user makes any invalid choice, then the default case will be executed.
- Then created separate methods to evaluate the area of the Rectangle, Square, and Circle.
Output
Now check it's output which is following.
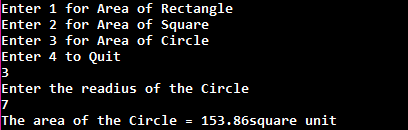
To exit the menu driven program, you can put a case in the switch case so that the program will quit and for that purpose, there is a predefined method System.exit(int) that you can use in order to achieve program termination.
So guys here I am wrapping up Menu Driven Program In Java. I hope you have a good understanding of how to write a menu driven code in Java. But still if you have any query then don't forget to drop your queries in comment section.
People Are Also Reading…
- How to Play Mp3 File in Java Tutorial | Simple Steps
- Tic Tac Toe Java Code Against Computer With Source Code
- Calculator Program in Java Swing/JFrame with Source Code
- Registration Form in Java With Database Connectivity
- How to Create Login Form in Java Swing
- Text to Speech in Java
- How to Create Splash Screen in Java
- Java Button Click Event
- Object-Oriented Programming in Java Questions and Answers
- Java Swing Password Field
gundersoncyricionsien.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.tutorialsfield.com/menu-driven-program-in-java/
0 Response to "Menu Driven Program in Java Example"
Post a Comment